Mars
Mars is a tensor-based unified framework for large-scale data computation which scales Numpy, Pandas and Scikit-learn,
see mars-repo for details. As a data computation framework, mars is easy to
scale out and can run across hundreds of machines simultaneously to accelerate large scale data tasks.
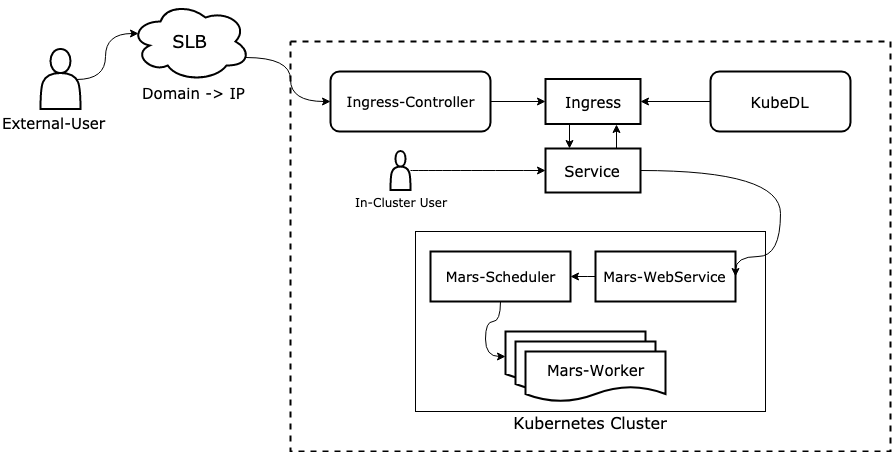
A distributed mars job includes 3 roles to collaborate with each other:
- WebService: web-service accepts requests from end-users and forwards the whole tensor-graph to scheduler, it provides a dashboard for end users to track job status and submit tasks interactively.
- Scheduler: scheduler compiles and holds a global view of tensor-graph, it schedules 'operands' and 'chunks' to workers.
- Worker: worker listen to 'operands' and 'chunks' dispatched by scheduler, executes the tasks, and reports results back to scheduler.
Run Mars with KubeDL
Run mars job on kubernetes natively.
1. Deploy KubeDL
Follow the installation tutorial
2. Apply Mars CRD
Mars CRD(CustomResourceDefinition) manifest file describes the structure of a mars job spec. Run the following to apply the CRD:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/alibaba/kubedl/v0.3.0/config/crd/bases/training.kubedl.io_marsjobs.yaml
3. Create a Mars Job
Create a YAML spec that describes the requirements of a MarsJob such as the worker, scheduler, WebService like below
apiVersion: training.kubedl.io/v1alpha1
kind: MarsJob
metadata:
name: mars-test-demo
namespace: default
spec:
cleanPodPolicy: None
webHost: mars.domain.com
marsReplicaSpecs:
Scheduler:
replicas: 1
restartPolicy: Never
template:
metadata:
labels:
mars/service-type: marsscheduler
spec:
containers:
- command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- python -m mars.deploy.kubernetes.scheduler
image: mars-image
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: mars
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
serviceAccountName: kubedl-sa
WebService:
replicas: 1
restartPolicy: Never
template:
metadata:
labels:
mars/service-type: marswebservice
spec:
containers:
- command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- python -m mars.deploy.kubernetes.web
image: mars-image
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: mars
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
serviceAccountName: kubedl-sa
Worker:
replicas: 2
restartPolicy: Never
template:
metadata:
labels:
mars/service-type: marsworker
spec:
containers:
- command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- python -m mars.deploy.kubernetes.worker
image: mars-image
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: mars
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 2
memory: 2Gi
serviceAccountName: kubedl-sa
status: {}
The spec field describes the requirement of each replica, including replicas, restartPolicy, template...and
the status field describes the job current status. Run following command to start an example mars job:
kubectl create -f example/mars/mars-test-demo.yaml
Check the mars job status:
$ kubectl get marsjob
NAME STATE AGE FINISHED-TTL MAX-LIFETIME
mars-test-demo Running 40m
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mars-test-demo-scheduler-0 1/1 Running 0 40m
mars-test-demo-webservice-0 1/1 Running 0 40m
mars-test-demo-worker-0 1/1 Running 0 40m
mars-test-demo-worker-1 1/1 Running 0 40m
4. Access web-service.
 Web service visualizes job status, computation process progress and provides an entry for interactive submission.
However, web service instance was running as a pod inside a kubernetes cluster which may not be accessible by external users.
Web service visualizes job status, computation process progress and provides an entry for interactive submission.
However, web service instance was running as a pod inside a kubernetes cluster which may not be accessible by external users.
KubeDL provides two access modes for users in different network environment.
4.1 Access web-service in-cluster.
For users in the same network environment with web service instance, they can directly access its service without any other additional configurations,
and the address is formatted as: {webservice-name}.{namespace}, it is a A record generated by CoreDNS, so you have to ensure that CoreDNS has been
deployed.
4.2 Access web-service outside cluster.
For users in different network environment(e.g. an internet user wants to access a mars web-service running in vpc),
users have to apply an SLB address first, so that they can ping the ip in vpc with a public address by SLB domain resolving, then in job spec, users just need fill the spec.webHost field with
their applied SLB address, KubeDLwill generated ingress instance with routing rules, so that external traffic can be routed to target web service and that
becomes available for outside users.
5. Memory Tuning Policy
Worker is the role that actually performs computing tasks in MarsJob.
Mars supports running jobs in different memory usage scenarios. For example, swap cold in-memory data out to spill dirs and persist in kubernetes ephemeral-storage.
Mars provides plentiful memory tuning options which has been integrated to MarsJob type definition, including :
- plasmaStore: PlasmaStore specify the socket path of plasma store that handles shared memory between all worker processes.
- lockFreeFileIO: LockFreeFileIO indicates whether spill dirs are dedicated or not.
- spillDirs: SpillDirs specify multiple directory paths, when size of in-memory objects is about to reach the limitation, mars workers will swap cold data out to spill dirs and persist in ephemeral-storage.
- workerCachePercentage: WorkerCachePercentage specify the percentage of total available memory size can be used as cache, it will be overridden by workerCacheSize if it is been set.
- workerCacheSize:WorkerCacheSize specify the exact cache quantity can be used.
users can set above options in job.spec.memoryTuningPolicy field:
apiVersion: training.kubedl.io/v1alpha1
kind: MarsJob
metadata:
name: mars-test-demo
namespace: default
spec:
cleanPodPolicy: None
memoryTuningPolicy:
plasmaStore: string # /etc/pstore/...
lockFreeFileIO: bool # false
spillDirs: []string # ...
workerCachePercentage: int32 # 80, indicates 80%
workerCacheSize: quantity # 10Gi
marsReplicaSpecs:
...
Run Mars in Standalone Mode
In standalone mode, a distributed Mars job are running standalone on bare hosts without the help of other container orchestration tools.
But this requires manual configuration effort and lack other abilities such as automatic failover of workers.
- run
pip install pymars[distributed]on every node in the cluster to install dependencies needed for distributed execution. - start different mars role processes on each node.
mars-scheduler -a <scheduler_ip> -p <scheduler_port>mars-web -a <web_ip> -p <web_port> -s <scheduler_ip>:<scheduler_port>mars-worker -a <worker_ip> -p <worker_port> -s <scheduler_ip>:<scheduler_port>
- usually there must be at least 1 web-service and 1 scheduler and a certain number of workers.
- after all processes started, users can open the python console run snippet to create a session with web-service and submit tasks.
import mars.tensor as mt
import mars.dataframe as md
from mars.session import new_session
new_session('http://<web_ip>:<web_port>').as_default()
a = mt.ones((2000, 2000), chunk_size=200)
b = mt.inner(a, a)
b.execute() # submit tensor to cluster
df = md.DataFrame(a).sum()
df.execute() # submit DataFrame to cluster
CRD Spec
Check the CRD definition. Go ->