Run in Host Network
Background
Network bandwidth is a bottleneck resource for communication-intensive jobs. Host mode networking can be useful to optimize performance. In addition, other scenarios (e.g: nvlink communications between containerized gpu processes) may depend on host network as well.
How To Use
KubeDL provides a feature-gate to enable hostnetwork mode for jobs. Users only need to add an annotation
kubedl.io/network-mode: host to the job specifications, for example:
apiVersion: "training.kubedl.io/v1alpha1"
kind: "TFJob"
metadata:
name: "mnist"
namespace: kubedl
annotations:
+ kubedl.io/network-mode: 'host'
spec:
cleanPodPolicy: None
tfReplicaSpecs:
Worker:
replicas: 3
...
Design
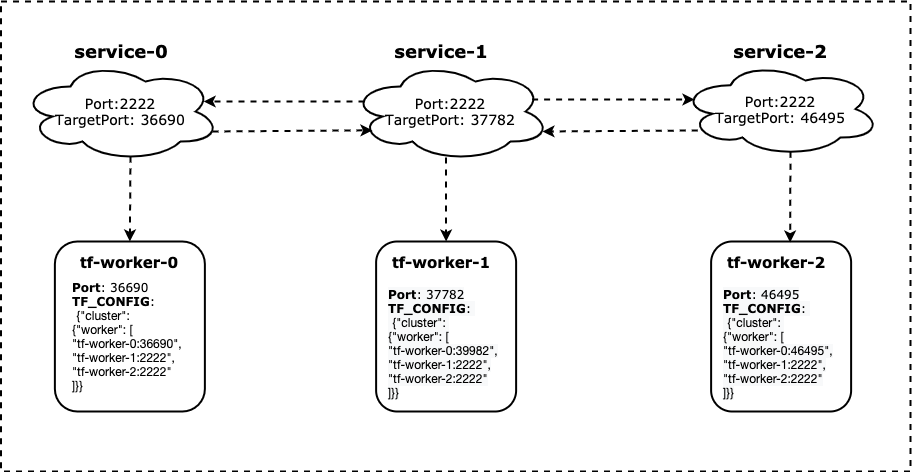
The essence of hostnetwork-mode is to randomize container ports to avoid port collision and enable service discovery
across workers. KubeDL achieves by following steps:
- Enable
hostnetworkinPodspec and set DNS policy asClusterFirstWithHostNet; - Choose a random port as container port.
- Change
TargetPortof corresponding worker'sServiceto the previous randomized port, and setCluterIPas empty string(instead ofNone), so that kube-proxy will be able to forward traffic fromPorttoTargetPort. - Change the job cluster spec (e.g. the
TF_CONFIG) . - Handle worker fail-over and use latest available port as the
TargetPortin the new worker.
Here is a Tensorflow job example: